TIM-3
発現および生理的な機能
- TIM-3は、細胞傷害性T細胞
 、制御性T細胞(Treg)
、制御性T細胞(Treg)  、NK細胞、並びに樹状細胞(DC)など、いくつかの抗原提示細胞(APC)
、NK細胞、並びに樹状細胞(DC)など、いくつかの抗原提示細胞(APC)  を含む、多種多様な免疫系の細胞に発現する免疫チェックポイント受容体です1,2。
を含む、多種多様な免疫系の細胞に発現する免疫チェックポイント受容体です1,2。
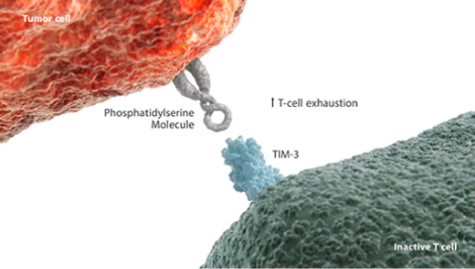
-TIM-3は、ホスファチジルセリン(PS)、CEACAM1(Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1)、ガレクチン-9、HMGB1(High mobility group box 1)などの多くのリガンドと相互作用します1,3。 - アポトーシスを起こした細胞では、PSによりT細胞の機能が障害されます4。
腫瘍浸潤性のDCにおけるPSまたはHMGB1とTIM-3の相互作用により、T細胞の活性化と炎症を惹起するDCの能力が障害される可能性が示唆されています4-6。 - 細胞傷害性T細胞上のTIM-3と、免疫抑制性のMDSC上のガレクチン-9との結合により、骨髄由来抑制細胞(MDSC)
 の増殖と抑制活性が増強されます1,7。
の増殖と抑制活性が増強されます1,7。 - T細胞でのTIM-3および共発現するCEACAM1の発現状況は、T細胞の疲弊化状態と相関しています1,8,9。
- TIM-3は自然免疫および獲得免疫の両方を抑制します1,6。
-TIM-3は、MDSC、TregおよびDCに作用することで、エフェクターT細胞の活性を間接的に抑制します1,7,10。 - Tregに発現するTIM-3は、T細胞の増殖および機能を低減させます10。
- NK細胞でのTIM-3発現の上昇は、NK細胞の疲弊にも関連しています1,11。
-さらに、NK細胞に発現するTIM-3は、PSまたはガレクチン-9と相互作用してNK細胞の機能不全をもたらします1,11,12。
がんでの役割
- NK細胞、T細胞およびTregにおけるTIM-3の発現上昇は、様々ながんで認められています11,13。
前臨床のエビデンス
- 前臨床データから、TIM-3の阻害によりNK細胞の活性が回復し、がん抗原のプロセシングが促進され、疲弊したT細胞が再活性化されて、その増殖および機能の回復が促進されることが示唆されています1,8,11。
- TIM-3は他の免疫チェックポイント受容体と共発現することが多く、TIM-3および他の免疫チェックポイント受容体を同時に阻害することで、疲弊したT細胞の再活性化が促進されることが示唆されています8,14,15。
REFERENCES–TIM-3
- Anderson AC, Joller N, Kuchroo VK. Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT: Co-inhibitory receptors with specialized functions in immune regulation. Immunity. 2016;44(5):989-1004.
- Han G, Chen G, Shen B, Li Y. Tim-3: an activation marker and activation limiter of innate immune cells. Front Immunol. 2013;4:449. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00449.
- Nakayama M, Akiba H, Takeda K, et al. Tim-3 mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cross-presentation. Blood. 2009;113(16):3821-3830.
- Freeman GJ, Casasnovas JM, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. TIM genes: a family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev. 2010;235(1):172-189.
- Maurya N, Gujar R, Gupta M, Yadav V, Verma S, Sen P. Immunoregulation of dendritic cells by the receptor T cell Ig and mucin protein-3 via Bruton's tyrosine kinase and c-Src. J Immunol. 2014;193(7):3417-3425.
- Chiba S, Baghdadi M, Akiba H, et al. Tumor-infiltrating DCs suppress nucleic acid–mediated innate immune responses through interactions between the receptor TIM-3 and the alarmin HMGB1. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(9):832-842.
- Dardalhon V, Anderson AC, Karman J, et al. Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway: regulation of Th1 immunity through promotion of CD11b+Ly-6G+ myeloid cells. J Immunol. 2010;185(3):1383-1392.
- Fourcade J, Sun Z, Benallaoua M, et al. Upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor antigen–specific CD8+ T cell dysfunction in melanoma patients. J Exp Med. 2010;207(10):2175-2186.
- Zhang Y, Cai P, Li L, et al. Co-expression of TIM-3 and CEACAM1 promotes T cell exhaustion in colorectal cancer patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;43:210-218.
- Gautron A-S, Dominguez-Villar M, de Marcken M, Hafler DA. Enhanced suppressor function of TIM-3+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(9):2703-2711.
- da Silva IP, Gallois A, Jimenez-Baranda S, et al. Reversal of NK-cell exhaustion in advanced melanoma by Tim-3 blockade. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2(5):410-422.
- Weber JK, Zhou R. Phosphatidylserine-induced conformational modulation of immune cell exhaustion-associated receptor TIM3. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13579. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14064-x.
- Anderson AC. Tim-3: an emerging target in the cancer immunotherapy landscape. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2(5):393-398.
- Lee J, Ahn E, Kissick HT, Ahmed R. Reinvigorating exhausted T cells by blockade of the PD-1 pathway. For Immunopathol Dis Therap. 2015;6(1-2):7-17.
- Sakuishi K, Apetoh L, Sullivan JM, Blazar BR, Kuchroo VK, Anderson AC. Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J Exp Med. 2010;207(10):2187-2194.